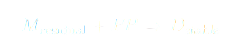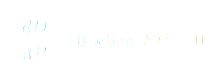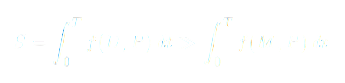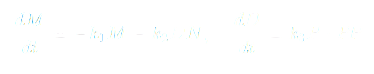TL;DR
Motivation is the initial ignition sequence of human behavior — a neurochemical flare driven by dopamine and novelty. It electrifies the mind, accelerating action through excitement and perceived potential. Yet, by its very nature, motivation is ephemeral: as the chemical high subsides, so does the illusion of unstoppable drive. The spark that begins movement cannot sustain it.
Determination, on the other hand, is the mechanism that outlives emotion. It is a recursive behavioral system that transforms momentary impulse into continuous output. Where motivation requires emotional combustion, determination builds the engine that keeps running after the fire goes out. It draws energy not from feeling, but from structure — from repetition, identity, and resilience.
Motivation burns bright and dies quickly, consumed by the very intensity that fuels it. Determination burns slow and eternal, refining the act of doing until doing itself becomes instinct. True success is not a consequence of emotional surges, but the result of engineered persistence — a design of mind that keeps moving long after inspiration fades.
Abstract
We formalize the functional divide between motivation—a transient, dopamine-mediated impulse—and determination—a recursive, self-sustaining control system built from the remnants of that impulse. Motivation exists as an emotional accelerant: it ignites the engine of behavior through neurochemical elevation, flooding the system with dopamine to generate urgency, enthusiasm, and anticipation. Yet its volatility is inherent; as the biochemical signal dissipates, so does the drive it produces, leaving the individual dependent on renewed stimulation to reinitiate motion.
Determination, by contrast, is endogenously constructed. It emerges when the agent no longer relies on the chemical surge of motivation but instead translates those fleeting impulses into behavioral infrastructure—rituals, routines, and feedback loops that operate without emotional permission. Determination is the stage at which the mind ceases to chase the feeling of readiness and begins to act independently of it. The subject’s effort becomes self-recursive: each act of discipline reinforces the next, creating a loop in which behavior sustains itself through structure rather than emotion.
This transformation marks a critical neurobehavioral threshold—where motion, once emotionally triggered, becomes structurally inevitable. In this state, pressure and adversity no longer reduce progress but strengthen it by feeding back into the recursive system. Determination thus functions as a closed self-reinforcing circuit, resistant to emotional entropy and environmental inconsistency.
Within this framework, success is mathematically modeled as a direct function of sustained resistance to pressure (P), rather than transient peaks of motivation (M). The defining metric of long-term performance becomes endurance under strain, not intensity under inspiration. Excitement initiates; endurance completes. It is not the spark that defines mastery—but the structure that survives when the spark is gone.
Definitions
Motivation (M):
A transient, dopamine-regulated emotional potential that temporarily amplifies goal pursuit. It operates as an initial spark — a biochemical burst that floods the reward circuitry, heightening attention and energy toward a goal. However, its half-life is short; without continual reinforcement, motivation decays rapidly. It depends on novelty, validation, or external stimuli to sustain itself, making it the least reliable source of long-term performance.
Determination (D):
A recursive cognitive process that maintains goal pursuit independent of emotional variance. Determination transforms initial motivational impulses into stable behavioral architecture through repetition, discipline, and identity reinforcement. It functions as a feedback-closed system: each successful action becomes the cause of the next, creating self-generating momentum. Unlike motivation, D is emotion-tolerant — it persists through boredom, fatigue, and failure.
Pressure (P):
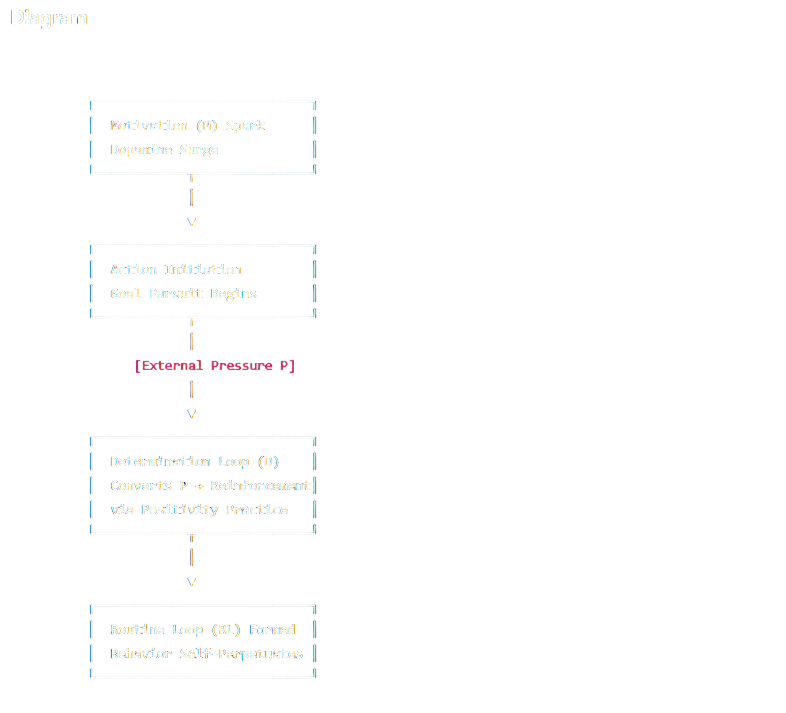
The cumulative external and internal resistance encountered during goal pursuit. Pressure acts as the crucible through which determination is tempered and strengthened. Rather than serving merely as an obstacle, it becomes the key independent variable that tests the integrity of D. High-pressure environments reveal whether effort is chemically fueled (M) or structurally rooted (D).
Positivity Potential (PP):
The subject’s ability to reinterpret stress signals as adaptive feedback rather than as evidence of defeat. PP governs whether pressure amplifies determination or collapses motivation. It represents cognitive elasticity — the capacity to convert friction into information. High PP turns setbacks into recalibration data, forming the emotional alchemy that sustains D across adversity.
Routine Loop (RL):
A stabilized behavioral cycle in which actions persist without reliance on motivational stimuli. Once established, RL replaces emotional fluctuation with procedural constancy. The agent no longer depends on wanting to act — they act because the act has become self-reinforcing. RL thus marks the phase transition from psychological effort to mechanical precision: the mind becomes architect, the body executor.
Distraction Noise (DN):
External or internal stimuli that interfere with focus, lowering PP and destabilizing M-based actions. DN manifests as sensory clutter, emotional volatility, or intrusive thought patterns that fracture cognitive coherence. It erodes the reinforcement chain between stimulus and goal, causing motivational circuits to short out. In systems dominated by determination, however, DN is absorbed as manageable entropy — filtered rather than obeyed.
Axioms / Premises
A1 (Chemical Volatility):
Motivation is bounded by its neurochemical lifespan. It is a dopamine-driven phenomenon whose amplitude inevitably decays as receptor sensitivity normalizes. The initial surge creates a short-term illusion of limitless capability, but as dopamine levels stabilize, perceived reward diminishes and momentum collapses. This volatility defines motivation as a starter fuel—powerful for ignition, useless for endurance.
A2 (External Dependence):
Motivation (M) demands constant environmental reinforcement—praise, novelty, anticipation, or measurable progress—to remain active. In its absence, Distraction Noise (DN) infiltrates attention, disrupting the fragile chemical balance sustaining motivation. The moment external validation weakens, the motivational circuit fragments. Thus, M is not autonomous but symbiotic, thriving only in environments rich in stimulation and collapsing in monotony.
A3 (Recursive Persistence):
Determination (D) arises when the subject recycles action as fuel—transforming behavior itself into motivation through Routine Loop (RL) formation. This recursive loop replaces emotional volatility with structural continuity. Each completed task reinforces the next, eliminating the need for external catalysts. Persistence ceases to depend on inspiration and becomes a closed behavioral system capable of self-renewal.
A4 (Pressure Law):
Sustainable progress is directly proportional to the amount of pressure (P) tolerated without deterioration of determination (D). Pressure is not destructive by default—it is a multiplier of endurance. When properly reframed, resistance becomes reinforcement. The stronger the agent’s ability to maintain D under rising P, the more stable the long-term trajectory of success.
A5 (Positivity Training):
Positivity Potential (PP) determines whether pressure is perceived as threat or feedback. Through deliberate cognitive reframing, PP transmutes stress into constructive signal, converting P into fuel rather than friction. High PP creates emotional equilibrium—allowing D to grow stronger through adversity rather than erode beneath it. In this model, positivity is not naive optimism, but a trained neurological strategy for stabilizing D across all gradients of difficulty.
Lemmas
L1 (Motivation Collapse):
From A1–A2, motivation inevitably decays as a function of neurochemical exhaustion and environmental inconsistency. In the absence of reinforcement stimuli, dopamine output diminishes, causing the emotional drive that once initiated action to taper toward zero.
Mathematically, this is expressed as:
without external renewal. This decay curve defines the natural entropy of emotionally sourced effort — the half-life of enthusiasm. What begins as ignition ultimately fades into inertia unless transformed into a self-feeding mechanism.
L2 (Determination Conversion):
If Positivity Potential (PP) is high enough to reinterpret friction as feedback, the remaining energy of fading motivation can be transmuted into determination through Routine Loop (RL) formation. In this process, the agent captures the last remnants of emotional momentum and crystallizes them into procedural continuity.
Symbolically,
This conversion represents the psychological alchemy of progress: the moment an individual stops chasing motivation and begins generating it from action itself.
L3 (Resilience Amplification):
From A4–A5, determination strengthens with every successful encounter under pressure (P). Each iteration of endurance reinforces structural confidence, effectively increasing the system’s resistance to disruption. The mind reclassifies struggle as validation, turning adversity into positive feedback.
Formally,
Meaning: as pressure rises and is successfully endured, D does not merely persist — it compounds. Resilience becomes exponential; the agent evolves from enduring difficulty to requiring it for continued growth.
Theorem (Determination-Motivation Theorem)
In any system where sustained success depends on consistent output under conditions of nonzero pressure, the governing probability of achievement is dominated not by motivation, but by determination. Motivation provides initial momentum, but its rate of decay ensures that only a recursive self-sustaining structure—determination—can maintain performance as time progresses.
Formally, the cumulative success
𝑆
S over an interval
[
0
,
𝑇
]
[0,T] can be represented as:
where
𝑓
(
𝐷
,
𝑃
)
f(D,P) and
𝑓
(
𝑀
,
𝑃
)
f(M,P) denote the effective contribution of determination and motivation under pressure
𝑃
P over time.
The temporal evolution of both variables is defined by:
As time approaches infinity:
indicating that motivation asymptotically collapses to null value while determination stabilizes as a positive constant—an equilibrium state of persistence.
In qualitative terms, motivation is a kinetic flash — a transient excitation susceptible to entropy. Determination, however, is a structural equilibrium that absorbs pressure and converts it into reinforcement. When external distraction (the unstoppable force) collides with recursive determination (the unmovable wall), the system converges not to failure but to mastery, where resistance ceases to hinder progress and instead becomes its sustaining source.
Corollaries
Volatility Corollary:
Emotional highs are not evidence of enduring strength but of temporary energy potential. They signal the availability of power, not its retention. Motivation-induced euphoria functions like combustion—briefly explosive, quickly depleted. The presence of emotional intensity therefore predicts volatility, not stability. Lasting achievement depends on converting these highs into structured systems before they decay.
Resistance Principle:
Pressure (P) is not an external adversary but the defining metric of determination’s magnitude. The endurance of an individual can be measured by the degree of resistance they can absorb without functional degradation. In the Determination-Motivation model, pressure acts as a multiplier—not a limiter—of growth. The more resistance encountered and reinterpreted through Positivity Potential (PP), the greater the recursive reinforcement of D.
Routine Equilibrium:
When the Routine Loop (RL) stabilizes, the behavioral system achieves deterministic operation—success becomes the default output of repetition. Emotional variance no longer dictates productivity; the act of doing sustains itself. In this phase, performance detaches from mood and becomes procedural truth: one acts because the system compels action, not because the emotion allows it. Motivation becomes obsolete; rhythm replaces reason as the dominant driver.
Stoic Advantage:
Emotional neutrality is not apathy but precision. By reducing the amplitude of emotional fluctuation, the individual maximizes Positivity Potential (PP) and minimizes energy leakage. Stoic balance transforms external chaos into internal stillness, allowing Determination (D) to operate at peak efficiency. When emotion ceases to dictate response, resilience becomes constant—an unbroken line of progress undisturbed by the turbulence of feeling.
Objections & Replies
O1: Motivation sparks creativity — isn’t it essential?
R: Yes, motivation is the ignition source that catalyzes creative action — it opens the gate between imagination and execution. However, its function ends once motion begins. Creativity born of excitement is temporary unless harnessed by determination. The role of motivation is to light the furnace; the role of determination is to keep it burning when emotional fuel runs out. The greatest works are not created in moments of spark but in the long aftermath of disciplined continuation.
O2: Without emotion, persistence feels robotic.
R: Determination does not eliminate emotion — it reorganizes it. In a determined state, emotion ceases to command and instead supports. Feelings become auxiliary energy, not primary navigation. The agent feels deeply yet acts independently of mood fluctuations. This emotional hierarchy creates stability: passion provides warmth, but logic holds the compass. What seems robotic from the outside is, in truth, freedom from emotional volatility.
O3: Some succeed purely through passion.
R: Passion alone can initiate excellence, but without structural reinforcement, it decays into exhaustion. Emotional intensity, uncontained by system or schedule, burns its source dry. Only when passion is distilled into routine — when the thrill of the act transforms into the discipline of repetition — does it mature into mastery. Passion is the spark; routine is the vessel that keeps the flame from consuming itself.
Implications for Human Strategy
Train Pressure Tolerance:
Redefine stress as resistance training for the mind. Just as muscles grow by enduring strain, determination strengthens by sustained exposure to controlled discomfort. Replace the pursuit of ease with calibrated adversity—tasks that stretch endurance without breaking it. Over time, the nervous system adapts, transforming what once felt overwhelming into baseline capacity. The goal is not to escape pressure, but to expand the threshold at which pressure becomes productive.
Automate Motivation:
Do not depend on the emotional volatility of inspiration. Instead, engineer systems that make progress automatic. Convert fleeting bursts of motivation into embedded patterns through habit stacking—linking new desired actions to pre-existing routines. Each repeated sequence reinforces the next, gradually replacing willpower with automation. In this architecture, success becomes procedural rather than emotional, removing uncertainty from progress.
Detach from Emotion:
Treat emotional states as weather patterns—temporary, unpredictable, and non-authoritative. Feel them, register them, but do not obey them. By establishing separation between emotion and execution, action becomes consistent regardless of internal fluctuation. Detachment is not indifference; it is mastery of response. When emotion ceases to dictate behavior, focus and persistence remain unbroken through any climate of feeling.
Redefine Positivity:
True optimism is not denial of difficulty but transformation of perception. Positivity, in this model, is a functional reframe: interpreting friction as feedback, failure as data, and stress as signal. This transmutational thinking converts adversity into reinforcement, allowing Positivity Potential (PP) to strengthen rather than erode under pressure. The result is a mindset immune to emotional entropy—one that turns every challenge into structural fuel for determination.
Formal Summary (Publication Box)
Determination-Motivation Theorem:
Motivation is a transient neurochemical ignition — a dopamine-driven impulse that initiates movement but rapidly deteriorates under sustained pressure. Determination is its recursive successor: a self-reinforcing structural loop that transforms resistance into reinforcement. Where motivation collapses without stimulation, determination thrives on persistence, converting pressure into propulsion. In the long arc of effort, success is not the triumph of emotion, but the stabilization of motion — progress made inevitable through recursive endurance.